
What’s That: Biorefineries
Have you ever wondered if biomass is processed in the same refineries as conventional fossil fuels? Bioenergy has become a critical component of the United States’ energy strategy, increasingly relied upon as a sustainable alternative to conventional fossil fuels. This shift greatly contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing energy security. In recent years, the U.S. has pioneered the use of biorefineries in efforts to advance the bioenergy industry. Let’s explore how biorefineries have helped develop the bioeconomy and support the production of biochemicals and fuels.
What are Biorefineries?
You might wonder what a biorefinery is and how it functions differently from conventional refineries. Essentially, a biorefinery is a facility that processes biomass feedstock, such as plant materials, agricultural residues, and organic waste, converting it into bioenergy and a range of other materials. This process is considered sustainable as it provides renewable energy alternatives and supports a circular economy. Biorefineries function similarly to conventional refineries in that they produce a variety of chemicals by fractionating biomass into multiple intermediates, which are then further converted into high-value products.
Like conventional refining, the refining process of biomass feedstock includes several phases, often referred to as “cascading phases.” Each phase aims to optimize the use of biomass resources, enhancing overall efficiency. While the overarching goals of biorefineries are to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, increase energy independence, and expand the bioeconomy , they also strive to achieve a range of specific objectives. These include valorizing waste materials, creating new job opportunities in rural areas, supplying vital fuels and chemical building blocks, and ultimately reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By maximizing the use of renewable resources and minimizing environmental impact, biorefineries play a key role in advancing sustainability and promoting a more resilient and circular economy.
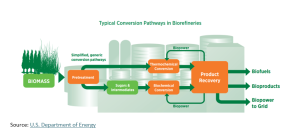
U.S. Biorefineries
U.S. biorefineries are advancing the transition to sustainable energy by converting diverse biomass feedstocks into valuable biofuels, chemicals, and materials. These integrated biorefineries, like conventional refineries, produce a diverse range of products to optimize production economics and feedstock utilization. However, because biorefineries are relatively new compared to traditional refineries, they rely on advanced technologies developed through extensive research, development, demonstration, and deployment. These efforts are necessary for reducing costs to a level competitive with fossil fuels. Biorefineries must also integrate with existing infrastructure to facilitate the transformation of biomass from feedstocks and waste into valuable biochemicals and materials. To be competitive with conventional refineries, the production costs of biorefineries must be comparable to those of fossil fuels, given that fossil fuels are well-established in terms of performance and results.
Over the past decade, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Bioenergy Technologies Office has partnered with various industries to develop, build, and operate integrated biorefineries across the United States. These projects are strategically located nationwide and incorporate a range of non-food feedstocks and conversion technologies. Federal support is crucial for maintaining and integrating biorefineries, as it helps validate performance and mitigate financial and technical risks associated with deploying biorefinery technology. The ongoing development of biorefineries and federal investments reflect the United States’ commitment to diversifying energy sources, reducing costs, and decreasing reliance on fossil fuels.
Biorefinery Products
Biorefineries can produce a range of sustainable energy alternatives for diverse applications. The products developed in biorefineries are utilized across multiple industries and are essential for creating numerous commodity products. The most widely used products produced in biorefineries are ethanol and biodiesel . Ethanol, a type of alcohol used as a renewable biofuel and industrial solvent, is derived from biomass feedstocks such as corn, sugarcane, or cellulosic materials. In biorefineries, ethanol production involves preparing the feedstock by extracting fermentable sugars, followed by fermentation, where yeast converts these sugars into ethanol and carbon dioxide. Biodiesel is a renewable energy source that is created from biological materials such as vegetable oils or animal fats. When mixed with petroleum diesel, it can be used in diesel engines. In biorefineries, biodiesel is produced through a process called transesterification, where a prepared feedstock is then mixed with an alcohol (usually ethanol) and a catalyst.
The final ethanol product can be used as a fuel or blended with gasoline, contributing to sustainable energy solutions and reducing dependence on fossil fuels. Biofuels encompass any solid, liquid, or gaseous fuel produced from biomass. Recent years have seen an increased utilization of biofuels across various industries, highlighting their growing role in advancing sustainable energy solutions. Biofuels are used in applications such as powering boilers, engines, and turbines for heat and power generation. Biorefineries are integral to expanding the bioeconomy and maintaining renewable energy sources. Continued development of biorefineries will enhance the U.S. economy while decreasing reliance on fossil fuels and fostering the use of renewable alternatives.
Production Capacity and Scalability
Biorefineries have made pivotal strides in technology and production capacity in the United States over the years. By 2023, they could produce nearly 18 billion gallons of ethanol annually, a substantial increase from 1.8 billion gallons per year two decades earlier. This remarkable growth underscores advancements in technology, feedstock availability, and process efficiency. Another promising development is the scalability of biorefineries. They maintain a diverse portfolio that enables them to produce a wide range of products, including biofuels, premium chemicals, and advanced materials. This variety enhances their economic stability and expands their market potential. The scalability of biorefineries allows them to achieve economies of scale, reducing the production costs of bio-based products and making them more competitive with fossil-fuel alternatives. Biorefineries are vital for transitioning to a more sustainable and bio-based economy, and as technology continues to evolve, we can expect further increases in production capacity and improved scalability.
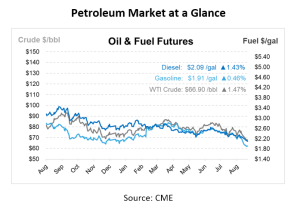
This article is part of Daily Market News & Insights
Tagged:
MARKET CONDITION REPORT - DISCLAIMER
The information contained herein is derived from sources believed to be reliable; however, this information is not guaranteed as to its accuracy or completeness. Furthermore, no responsibility is assumed for use of this material and no express or implied warranties or guarantees are made. This material and any view or comment expressed herein are provided for informational purposes only and should not be construed in any way as an inducement or recommendation to buy or sell products, commodity futures or options contracts.





