
What Is It – Batching
Have you ever wondered how different types of fuels make their way from refineries to gas stations, airports, and other destinations where they are needed? It’s not as simple as you might think! The journey involves an intricate process that maximizes efficiency while minimizing costs. In this What Is It Wednesday article, we will explore the tedious world of fuel transportation, focusing on a key concept known as batching.
What is a Batch?
In the realm of pipelines, “batching” refers to a method by which different types of liquid petroleum are transported through the same pipeline. Rather than having a dedicated pipeline for each type of fuel, operators send various products in “batches.” For example, an operator might send gasoline through the pipeline for several hours, then switch to jet fuels, before finally transitioning to diesel fuel.
This method is a cost-effective way for pipeline operators to transport multiple types of fuel without the need for multiple pipelines. It also provides greater flexibility, as operators can adjust the types and quantities of fuel they send based on demand.
Consider a gas station that offers both gasoline and diesel fuel. The station owner purchases fuel from a supplier that uses a pipeline to transport the fuel. In this case, the supplier might send a batch of gasoline to the station, followed by a batch of diesel fuel. This allows the station owner to receive both types of fuel through the same pipeline, saving on transportation costs and ensuring a steady supply of both gasoline and diesel fuel for their customers.
How does batching work?
Pipeline companies have fixed specifications for each product batched for shipping. These specifications include factors like viscosity (the degree to which the liquid resists flow), density (distinguishing between heavy and light products), temperature, volatility, sulfur content, and sediment-and-water content.
Here’s a step-by-step look at how batching actually works:
- The pipeline operator sends a batch of one product, such as gasoline, through the pipeline for several hours.
- Once the gasoline has moved through the pipe, the operator switches to a batch of diesel.
- After a few more hours, another shift can occur, and so on.
- The pipeline operator uses scheduling to keep track of batches and ensure that customers’ products are properly handled.
- In cases where mixed products occur, called transmix, they must be placed in a separate tank and reprocessed to separate the different components.
- While some pipeline systems utilize a batch mechanism known as a “pipeline pig” to separate individual parcels, the usual approach is to mix together “like products” in a common stream.
How Batching Prevents Commingling
When transporting different types of fuel through a pipeline, preventing them from mixing together—a scenario known as commingling—is important to maintain the integrity of each distinct fuel type. This is where the process of batching comes into play. Batching allows different types of fuels to be sent through the pipeline in separate, distinct segments, ensuring that gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and other petroleum products remain separated from each other. To further prevent commingling, pipeline operators can use a range of methods, such as employing pipeline pigs—a kind of separator tool that moves with the fuel flow—to create physical barriers between batches. These methods ensure that each batch of fuel remains pure and uncontaminated, arriving at its destination in the same condition as when it entered the pipeline.
How does batching impact my fuel costs?
The answer lies in lower energy costs. By making efficient use of existing pipeline capacity, batching reduces the need for multiple product-specific pipelines. This, in turn, lowers the cost of transporting oil and its by-products. Batching also has an important safety aspect. Reduced volumes of oil products transported by rail and trucks—known to be more costly and less safe means of energy transportation—further emphasize the benefits of this innovative delivery method.
The world of fuel buying and pipeline operation is intricately connected, with batching playing a vital role in ensuring that the process is as efficient, cost-effective, and safe as possible. From gas stations and airlines to manufacturing plants, customers across various industries rely on the seamless operation of batching to receive the fuel they need for their operations.
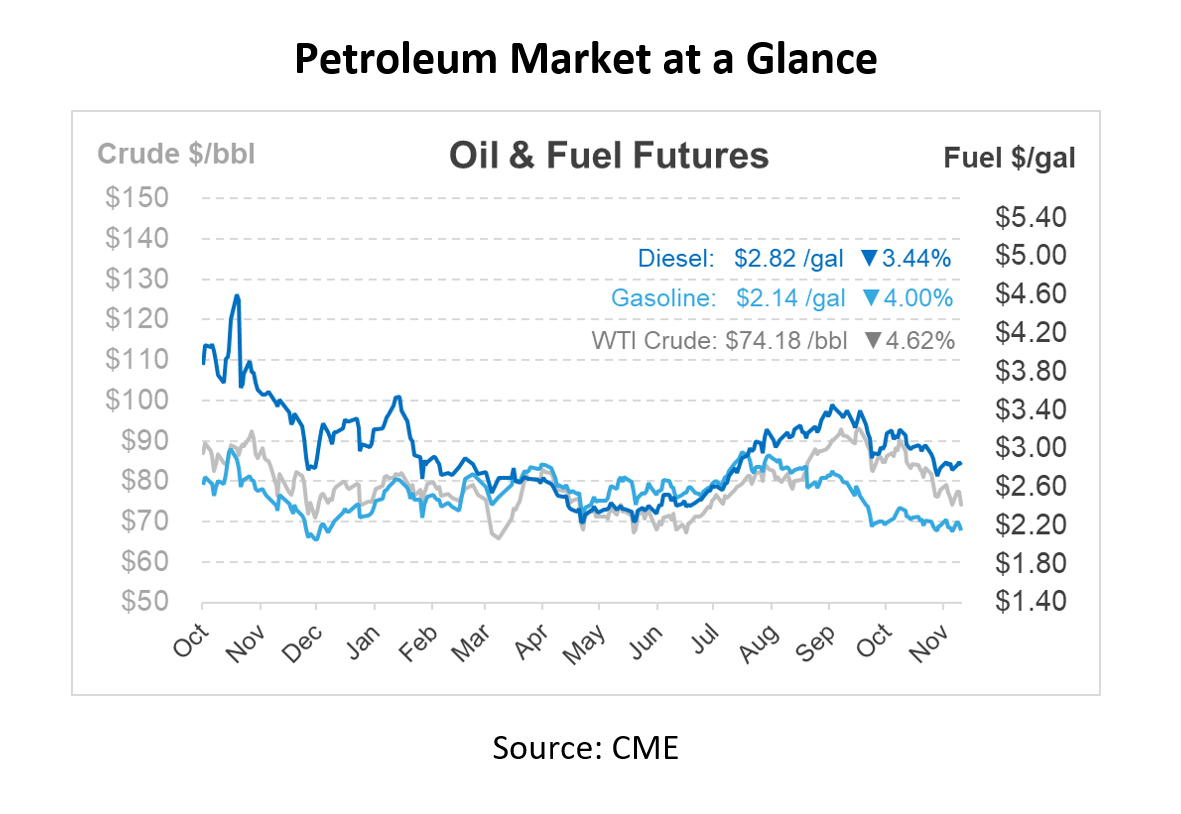
This article is part of Daily Market News & Insights
Tagged: Daily Market News & Insights, diesel, fuel prices, gasoline, Inventories, oil prices, pipeline, prices, Supply
MARKET CONDITION REPORT - DISCLAIMER
The information contained herein is derived from sources believed to be reliable; however, this information is not guaranteed as to its accuracy or completeness. Furthermore, no responsibility is assumed for use of this material and no express or implied warranties or guarantees are made. This material and any view or comment expressed herein are provided for informational purposes only and should not be construed in any way as an inducement or recommendation to buy or sell products, commodity futures or options contracts.





