Even as renewables increase, fossil fuels continue to dominate U.S. energy mix
Editor’s Note: Renewable energy has demonstrated impressive growth in recent years; however, renewables still have a long way to grow before they can rival fossil fuels. Renewable energy providing electricity is still unreliable – since weather is unpredictable, fossil fuels must continue providing baseload energy. In electricity, the key barrier to renewable growth is improving energy storage methods so energy created by the sun can be stored during the day and released at night.
For fuels, renewable sources still suffer from quality control concerns. While products like renewable diesel are a drop-in replacement for petroleum products, products like ethanol and biodiesel both suffer from lower energy content and fuel quality concerns. For renewables, more work must be done to address reliability and quality before renewables can truly compete with fossil fuels.
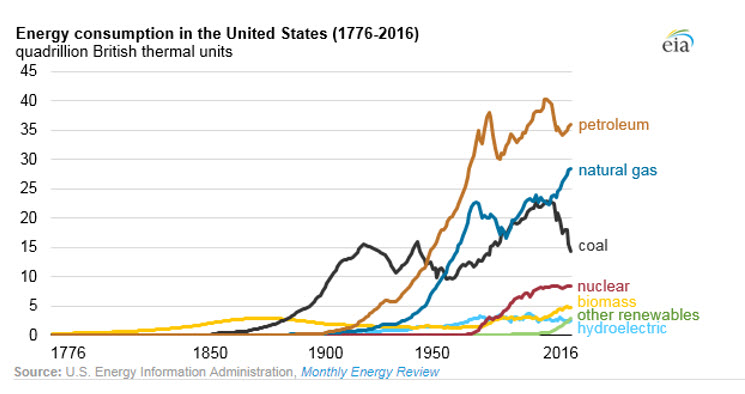
Fossil fuels have provided more than 80% of total U.S. energy consumption for more than 100 years. Since 1928, when consumption of natural gas surpassed that of biomass, the three fossil fuels—petroleum, natural gas, and coal—have been the most consumed fuels in the United States. In 2016, fossil fuels accounted for 81% of total U.S. energy consumption, the lowest fossil fuel share in the past century.
In 2016, the renewable share of energy consumption in the United States was 10.5%. This was the largest renewable share since the 1930s, when overall energy consumption was lower and the amount of biomass consumption (mainly wood) was relatively high. The greatest growth in renewables over the past decade has been in solar and wind electricity generation. Liquid biofuel consumption—more than half of which is ethanol blended into motor gasoline—has also increased in recent years, contributing to the growing renewable share of total energy consumption.
In addition to the increasing share of renewables, the decline in the fossil fuel share of consumption is attributable mainly to declines in coal consumption. U.S. coal consumption fell nearly 9% in 2016, following a 14% drop in 2015. Overall, U.S. coal consumption has declined almost 38% since 2005. In each of the past 20 years, the power sector has accounted for more than 90% of total U.S. coal consumption.
Petroleum, which encompasses nearly all transportation fuels and several petroleum-based fuels used in homes, businesses, and industries, continues to be the largest source of energy consumption in the United States. Petroleum consumption has increased in each of the past four years.
Consumption of natural gas has risen in 9 of the past 10 years. As recently as 2006, the United States consumed more coal than natural gas (in energy-equivalent terms), but as natural gas consumption has increased—particularly in the electric power sector—natural gas use in 2016 was about twice that of coal.
This article is part of Daily Market News & Insights
Tagged:
MARKET CONDITION REPORT - DISCLAIMER
The information contained herein is derived from sources believed to be reliable; however, this information is not guaranteed as to its accuracy or completeness. Furthermore, no responsibility is assumed for use of this material and no express or implied warranties or guarantees are made. This material and any view or comment expressed herein are provided for informational purposes only and should not be construed in any way as an inducement or recommendation to buy or sell products, commodity futures or options contracts.